Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Time series of postProcessing coefficient force
This example reads and plots one postProcessing coefficient force and compute and plot the fft of the lift coefficient force
Read the postProcessing files
Note
In this example it reads one postProcessing file for the statistically steady state of the flow around a rectangular cylinder.
from fluidfoam.readpostpro import readforce
import numpy as np
# ****************Selection of case, repository and parameters*************** #
rep = '../output_samples/'
case = 'ascii'
time = '100' # Simulation start time for fft
force_file_name = 'coefficient' # Variable on which fft is applied
index_Cl = 2 # Lift force
index_Cd = 1 # Drag force
n0 = 0 # Start point for the fft
nfft = 500 # Number of point for the fft
calculdeltat = 0.01 # Delta t used in the calculation
fftdeltat = 0.2 # Sampling Delta t for the fft, note that Tfft = nfft * fftdeltat =< Ttot = endTime - time
timestart = 0 # Start time for sampling from time
display_temp = True
# *************************************************************************** #
# reading Data
force = readforce(rep + case, namepatch = 'forces', time_name = time, name = force_file_name)
timevec = np.zeros(len(force))
varC = np.zeros((len(force),2))
for i in range(len(force)):
timevec[i] = force[i,0]
varC[i,0] = force[i,index_Cl]
varC[i,1] = force[i,index_Cd]
# Sampling
i = 0
varCi = np.zeros((nfft,2))
vart = np.zeros(nfft)
while i < nfft:
for k in range(2):
varCi[i,k] = varC[int(i*fftdeltat/calculdeltat+timestart/calculdeltat), k]
vart[i] = timevec[int(i*fftdeltat/calculdeltat+timestart/calculdeltat)]
i += 1
# fft calculation
y1 = np.zeros((nfft,2),dtype = np.complex128)
for k in range(2):
# Division by nfft to correct the spectral amplitude
y1[:, k] = np.fft.fft(varCi[n0:n0+nfft,k] - np.mean(varCi[n0:n0+nfft,k]))/nfft
Now plots the lift and drag coefficient forces
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 20})
# Temporal plot section
colorList = ['r', 'b']
labelList = ['Lift', 'Drag']
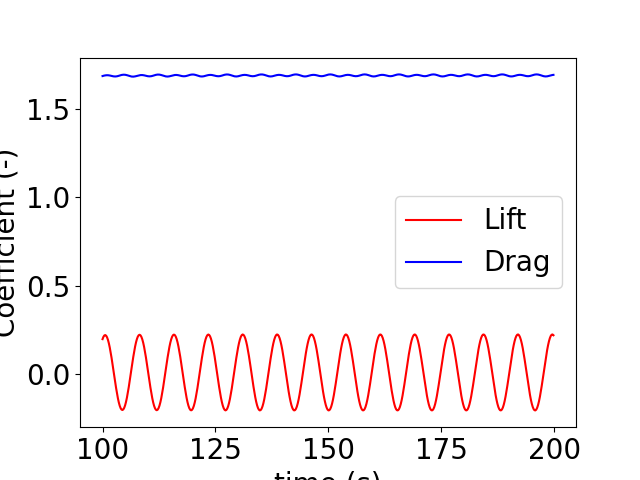
if display_temp:
for k in range(2):
plt.plot(vart[n0:n0+nfft], varCi[n0:n0+nfft,k],
color = colorList[k], label = labelList[k])
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Coefficient (-)')
plt.show()
# frequency plot section
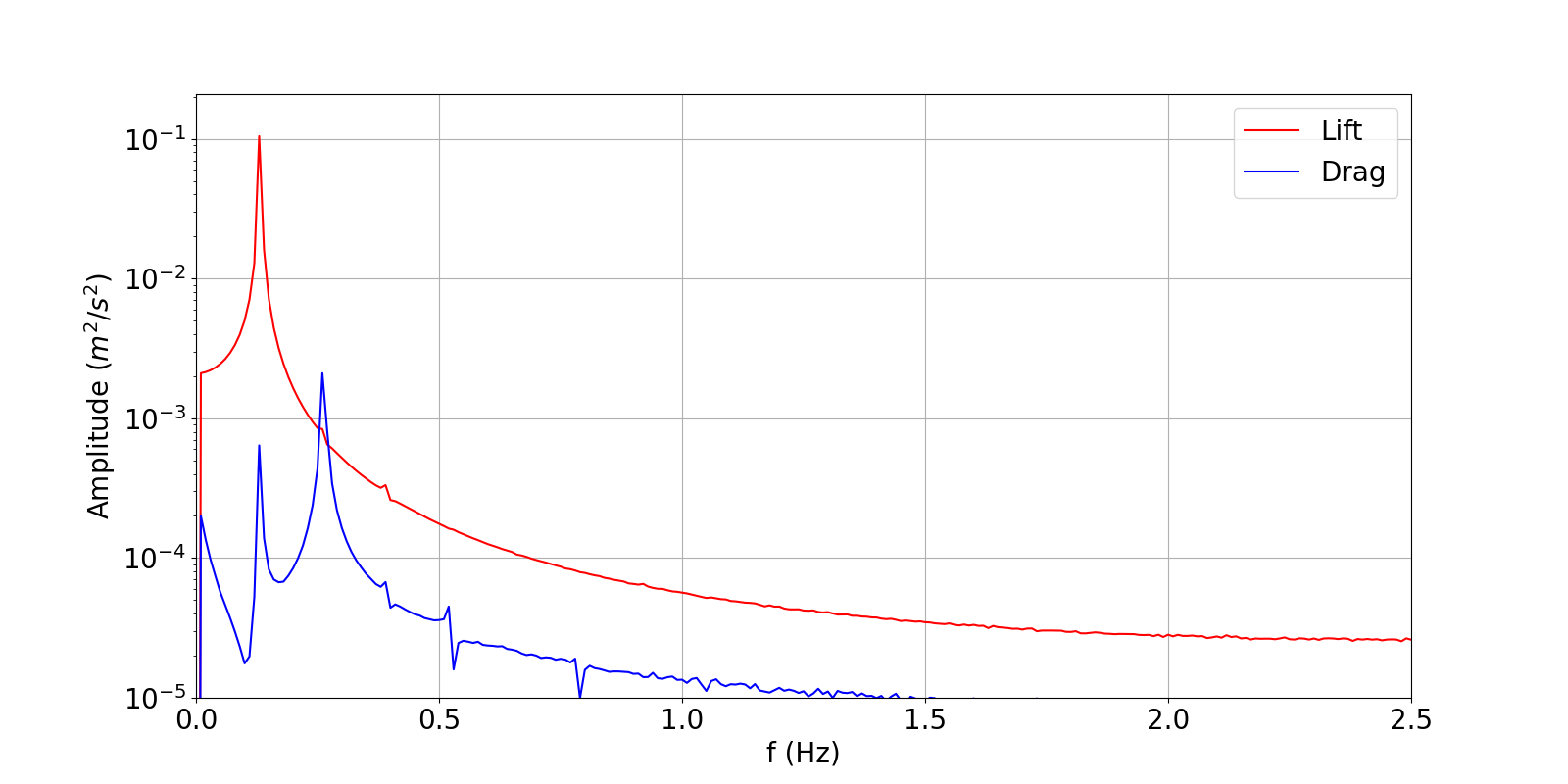
f = np.arange(nfft)*1/(fftdeltat*nfft)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 8))
for k in range(2):
plt.semilogy(f[n0:n0+nfft], abs(y1[n0:n0+nfft,k]), color = colorList[k], label = labelList[k])
plt.axis([0.0, 1/(2*fftdeltat), 1e-5, 2*np.max(abs(y1[n0:n0+nfft]))])
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.xlabel(r'f (Hz)')
plt.ylabel(r'Amplitude ($m^2/s^2$)')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.709 seconds)