Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Create vectorised visualisations of the mesh
This example shows how to use MeshVisu object to plot vectorised images of 2D planar meshes.
First create a visualisable mesh object with MeshVisu
Note
This class allows you to create a list of edges contained inside a box. This list of edges will then be ploted.
# import the class MeshVisu
from fluidfoam import MeshVisu
# path to the simulation to load
path = '../../output_samples/pipeline'
# Load mesh and create an object called myMesh
# The box by default is egal to the mesh dimension
myMesh = MeshVisu( path = '../../output_samples/pipeline')
Reading file ../../output_samples/pipeline/constant/polyMesh/faces
Reading file ../../output_samples/pipeline/constant/polyMesh/points
Box set to mesh size:
(minx, miny, minz) = (-0.75, -0.1, -0.001)
(maxx, maxy, maxz) = (1.0, 0.205, 0.0)
Plot the whole mesh
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.collections import LineCollection
# compute mesh aspect ratio:
xmin, xmax = myMesh.get_xlim()
ymin, ymax = myMesh.get_ylim()
AR = (ymax - ymin) / (xmax - xmin)
fig, ax = plt.subplots( figsize = (8,8*AR))
# create a collection with edges and print it
ln_coll = LineCollection(myMesh.get_all_edgesInBox(), linewidths = 0.25, colors = 'brown')
ax.add_collection(ln_coll, autolim=True)
# impose the dimensions of the box as the limits of the figure
ax.set_xlim(myMesh.get_xlim())
ax.set_ylim(myMesh.get_ylim())
# to avoid distorting the mesh:
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# to don't print axis:
ax.axis('off')

(-0.75, 1.0, -0.1, 0.205)
Update the box to zoom on the cylinder and save figure
myMesh.update_box(((0, 0, -1), (0.03, 0.03, 1)))
fig, ax = plt.subplots( figsize = (8,8))
# create a collection with edges and print it
ln_coll = LineCollection(myMesh.get_all_edgesInBox(), linewidths = 0.25, colors = 'black')
ax.add_collection(ln_coll, autolim=True)
# Set box dimensions as the figures's limits
ax.set_xlim(myMesh.get_xlim())
ax.set_ylim(myMesh.get_ylim())
# to avoid distorting the mesh:
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# to don't print axis:
ax.axis('off')
# to save the figure in pdf or svg format, uncomment one of the following two lines:
# plt.savefig('./myCylinderZomm.pdf', dpi=fig.dpi, transparent = True, bbox_inches = 'tight')
# plt.savefig('./myCylinderZomm.svg', dpi=fig.dpi, transparent = True, bbox_inches = 'tight')
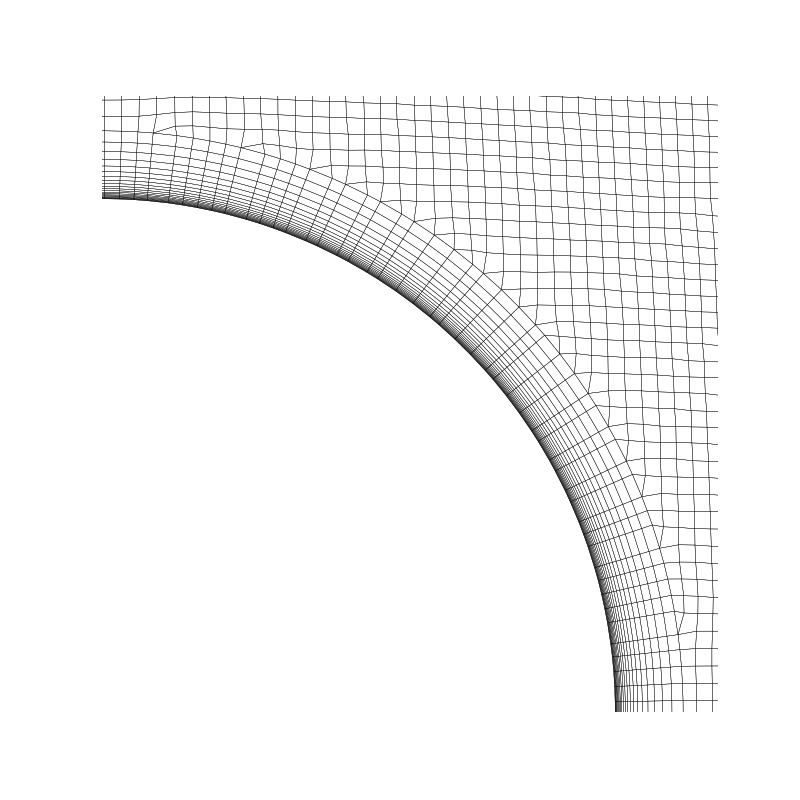
(0.0, 0.03, 0.0, 0.03)
Visualisation of dynamic case in xz plane
# path to the simulation to load:
mypath = '../../output_samples/darrieus'
# time folder for which you want to display the mesh:
mytime = '0.1'
# plane in which the mesh is contained, either:
# 'xy': the xy-plane of outgoing normal z (default value)
# 'xz': the xz-plane of outgoing normal -y
# 'yz': the yz-plane of outgoing normal x
myplane = 'xz'
# box to zoom in on for mesh display:
mybox = ((-1.2, -1, -1.2), (1.2, 1, 1.2))
# Load mesh and create an object called myOtherMesh:
myOtherMesh = MeshVisu(path = mypath, box = mybox, time_name = mytime, plane = myplane)
# The next line sets the thumbnail for the last figure in the gallery
# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = -1
fig, ax = plt.subplots( figsize = (8,8))
# create a collection with edges and print it
ln_coll = LineCollection(myOtherMesh.get_all_edgesInBox(), linewidths = 0.25, colors = 'black')
ax.add_collection(ln_coll, autolim=True)
# Set box dimensions as the figures's limits
ax.set_xlim(myOtherMesh.get_xlim())
ax.set_ylim(myOtherMesh.get_zlim())
# to avoid distorting the mesh:
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# to don't print axis:
ax.axis('off')
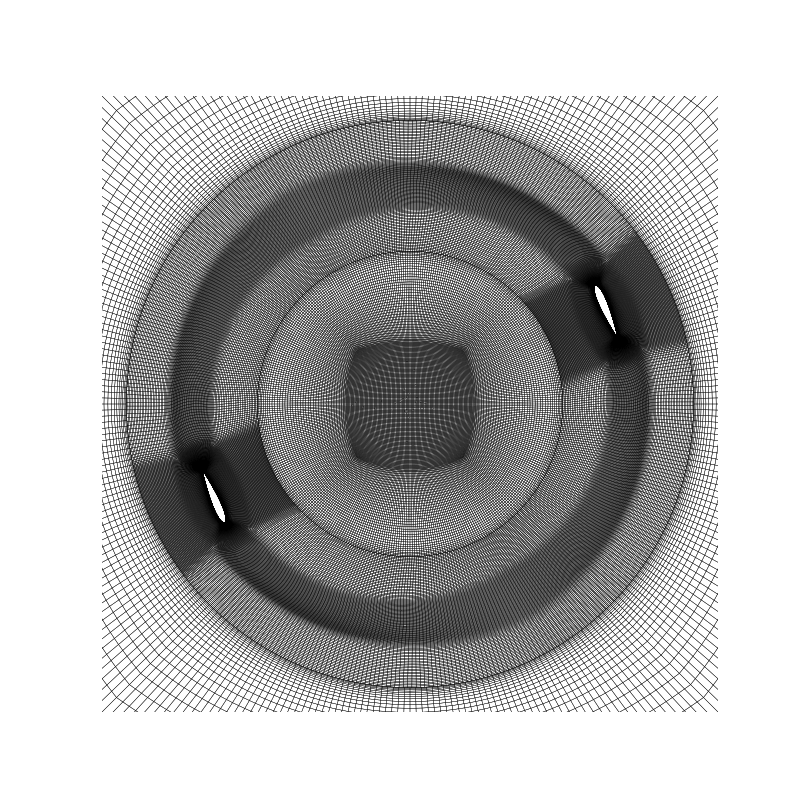
Reading file ../../output_samples/darrieus/constant/polyMesh/faces
Reading file ../../output_samples/darrieus/0.1/polyMesh/points
(-1.2, 1.2, -1.2, 1.2)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 41.128 seconds)